Gigabyte External Hard Drive Unveils The Limited Edition Portable Devices

One Gigabyte (GB) (GB) — or pronounced with two hard GaAs a measure of storage capacity for data that is approximately equivalent to one billion bytes. If you use decimal notation (base 10), one Gigabyte equals exactly 1 million bytes. If you use the binary form (base 2), one Gigabyte is equivalent to 230 bytes which are 1,073,741,824. Giga originates from the Greek word meaning gigantic. Werner Buchholz is credited with the byte 1956 while assisting in the design of IBM’s 7030 Stretch. It was the first supercomputer that was transistorized.
A gigabyte has been the most common dimension of capacity in storage devices for data since the late 1980s. In recent times the terabytes (TB) are now the most common form of measuring storage capacity, particularly in the case of HDDs (HDDs) along with solid-state drives (SSDs).
Cloud providers and hardware manufacturers are still referring to the costs of storage capacity by the value per Gigabyte, but that’s gradually changing to costs per Terabyte. Nowadays, HDDs or flash SSDs can store many gigabytes worth of data, or even thousands of gigabytes; that’s what has led to it’s no surprise that TB designation has been slowly replacing GB in numerous instances.
More Articles: What is External Storage Devices? Types and Reviews.
What exactly is a gigabyte simply in terms of definition?
A gigabyte is a data size equivalent to roughly one billion bits of information. The term “gigabyte” is commonly used to refer to the quantity of stored data or the capacity of a storage device.
For instance, an HDD might have 500GB of capacity, but it has a total of only 200GB worth of information. Apart from the stored data, gigabytes can be used for the amount of data transferred and storage capacity.
Typical data storage measurements for data
The Gigabyte, just like other measurements of data, is based on the word byte. It corresponds to up to eight bits. The Gigabyte is comparable to the following measurement standards:
1 megabyte (decimal) (or 1,024 megabytes) (binary);
1,000,000 Kilobytes (decimal) equivalent to 1,048,576 Kilobytes (binary) and
1,000,000,000,000 bytes (decimal) or 1,073,741,824 bytes (binary).
The measurements of data capacity more significant than a gigabyte comprise the following:
A Terabyte is equivalent to 1 gigabyte (decimal) (decimal) or 1 024 gigabyte (binary).
A petabyte equals one million gigabytes (decimal) or 1,048,576 gigabytes (binary).
A single exabyte equals 1000,000,000 gigabytes (decimal) or 1,073,741,824 gigabytes (binary).
Different ways in which gigabytes are measured

The distinction between the decimal and the binary number has led to a lot of confusion for consumers, especially when they encounter terms such as mebibyte or kibibyte. gibibyte, or Tebibyte.
Network, computer, and storage systems use two standards to determine the number of bytes per Gigabyte: base ten and base 2. Base 10’s definition of a Gigabyte utilizes the decimal system to demonstrate that 1GB equals 109 bytes, equivalent to 1 trillion bytes. Today, most storage makers and users employ the base 10 standards to define Gigabyte.
Computers and operating systems typically employ the base 2 or binary type of measurement where 1 GB is 1,073,741,824 bytes. In this case, the term gigabyte can be called gibibytes, though a few vendors use this approach, leading to confusion. It wasn’t necessary at the beginning of storage because the disparity between the base ten measurements and the bottom 2 was insignificant. However, the differences increased as companies began producing storage media that had more capacity.
Binary Vs. Decimal measurement of data
Base 2 (binary) as opposed to. The base 10 (decimal) measurements Due to the differences in the standards, users may find discrepancies regarding how storage is described. For instance, a company may display that the storage capacity on the HDD at 500GB; however, the computer would report that the HDD’s capacity is 466 GB. However, most systems make use of GiB when referring to gibibytes. This helps make clear the distinctions.
How long will it take to make use of 1GB of data?
In today’s highly data-intensive work, one Gigabyte of data can be consumed quickly. A single-layer digital media disk (DVD) can store just 4.7 gigabytes of information, and a double-layer disk can contain only 8.5 GB, a slight drop in the bucket compared to a 10-TB HDD. Even a standard desktop or laptop computer has just 8 GB or 16GB of RAM.
In more precise terms, the concept of a gigabyte is equivalent to the following:
250 songs downloaded;
6,180 received and sent emails;
250 10-megapixel photos;
Average email 50,000 with no attachments;
3333 average emails, with wings of standard size;
5 hours of standard-definition films 5 hours of standard-definition movies
353 YouTube videos that are one minute long.
Storage capacity examples from the real world
What is a GB on a smartphone?
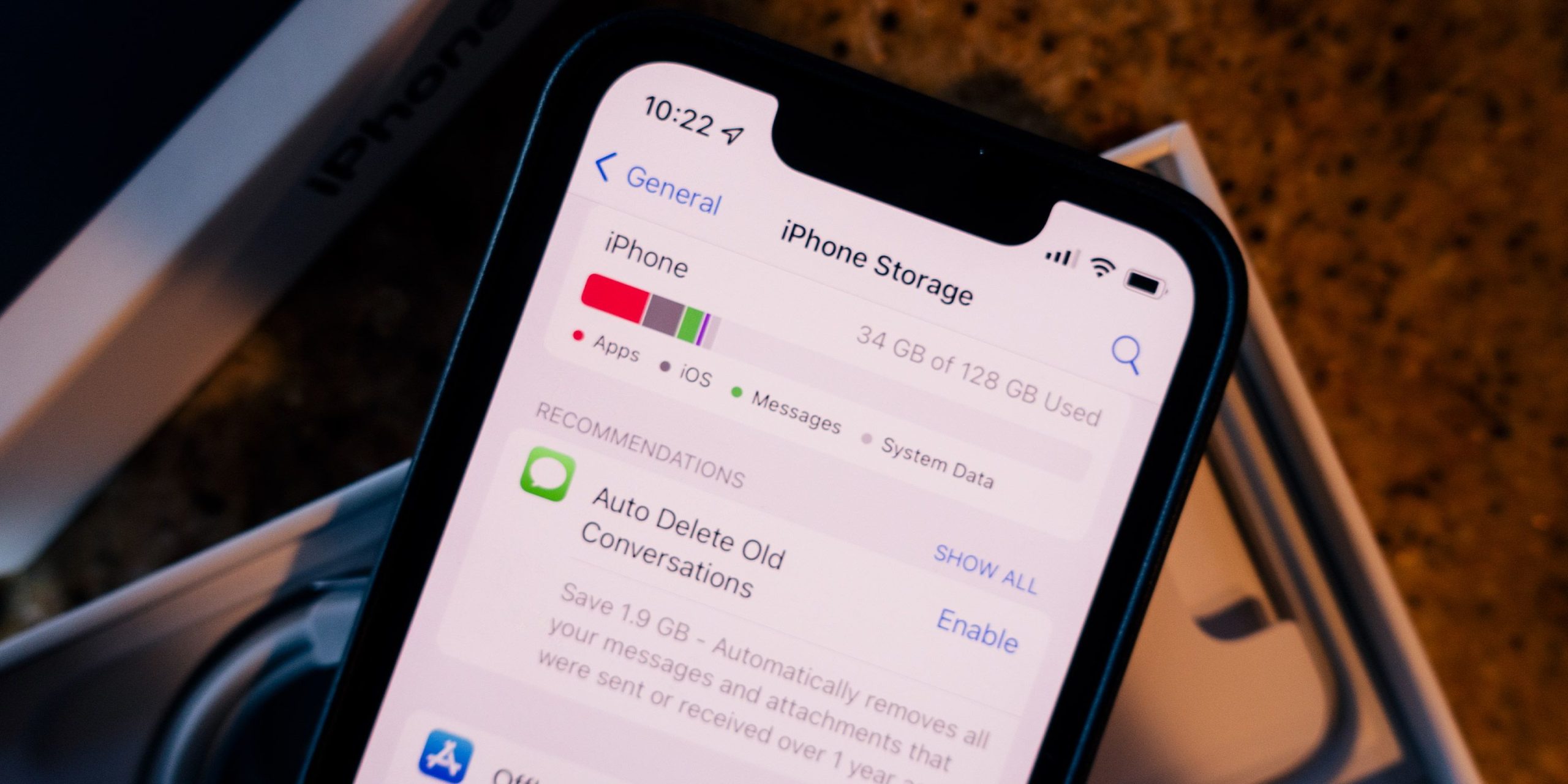
When purchasing smartphones, buyers typically have the option of choosing from several capacities of storage that are usually dependent on the number of gigabytes available—the greater the number of gigabytes available, the greater the storage capacity and the higher price.
For many customers, storage capacity is typically one of the main aspects of choosing a smartphone. For instance, Apple’s iPhone 13 Pro offers four capabilities: 128 GB, 256GB, 1 TB, and 512GB, as well as Samsung’s Galaxy Z Flip3 comes with only two options: 128 GB or 256GB. Most smartphones today employ gigabytes as a measure of storage capacity; however, according to what this iPhone 13 Pro indicates, it’s only an issue of time before Terabytes replace Gigabytes.
Regardless of the storage option the user chooses, they must be aware that the available capacity is typically smaller than the capacity. For instance, the iPhone could require between 11 and 14GB of storage for iOS and preinstalled apps. The amount will vary based depending on the model and setting. Software updates can also impact the available capacity.
Additionally, gigabyte measurements could be a factor in determining consumers of smartphones select their plans for cellular services. Nowadays, many plans offer unlimited texting and calls. However, they limit how much data can be transmitted to and to or. The amount of data is often the main difference between plans.
For example, T-Mobile offers the Essentials, Magenta, and Magenta MAX plans. The Essentials plan comes with 50GB of data. The Magenta plan gives 100GB, and the MAX plan offers unlimited data. Additionally, the Magenta plan comes with up to 5GB of hotspot data for mobile devices, and the MAX plan comes with 40GB of high-speed data and unlimited data speeds at 3G.
In the current market, gigabytes have a significant role in selecting mobile products and services. However, it could be a while until the conversation turns to Terabytes instead of gigabytes. In the meantime, users must be aware of the available GB options for their mobile phones.
History of Gigabyte
The first gigabyte-capacity hard disk came from IBM 3380, which was launched in the year 1980. IBM 3380 packaged two 1.26 GB hard disks in an appliance-sized cabinet. Prices ranged from $81,000 to $142,000, based on the model.
When computers were first introduced, HDDs were relatively small in capacity and very expensive. IBM Personal Computer XT, which was released in 1983 was the first computer with a built-in hard disk as an integral feature. It was initially equipped with a 10 megabyte (MB) (or 20MB) hard disk. In 1991 the first 1 GB drives were made available for purchase at almost $3000.
Since then, the capacity of Gigabyte External Hard Drives has increased rapidly, and prices have dropped almost as quickly. When Hitachi introduced the first 1TB drive in 2007, the company stated that it required 35 years to get HDDs to reach 1GB and 14 years to grow up to 500 GB. The first drives with 1TB capacity came out just two years later. Presently, HDDs are available with 20TB of storage SSDs can accommodate up to 100 TB of storage.
Gigabyte vs. gigabit

But, abbreviated as a binary digit, it is a minor type of computer data. Bits are only one binary number that can be either 0 or. Computers are built to store data and execute instructions using bits multiples, also known as bytes. Most computer systems have 8 bits per byte and 8,589,934,592 bits within one Gigabyte.
A byte — and, in turn, Gigabyte usually refers to data in a state of rest, but it can also describe the transfer of data between computer systems or storage throughput or bandwidth. For instance, computer memory and storage are usually measured in bytes—for example, an office computer with 16 GB of RAM and a storage capacity of 750 GB.
In most computer systems, one byte is the smallest addressable unit in memory. For example, an 820 MB hard drive can hold 820 million bytes of information.
The term “bit” — or, in turn, gigabit usually refers to data that is transferred over networks. For example, gigabits can be used to define the speed of data transfer, for instance, network throughput and speed of internet connections, for example, 10 gigabits second or 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
Pricing and options for Gigabyte-sized storage
A variety of storage media offer gigabyte capacity, and the total can vary significantly. The most widely used storage options included in this list are HDD flash drives, memory card USB memory sticks, Blu-ray discs, and DVDs.
Techopedia explains Gigabyte (GB or GByte)
A byte comprises eight bits, which are made up of the string of 0s and 1s. The eight bits could hold up to 256 numbers, which range between 0 and 255. A byte is the number of bits used to encode one text character.
Under the International System of Units (SI from French: Systeme International d’Unites), The “Giga” prefix refers to one billion (109 or 1,000,000,000) bytes. In computing terms, “gigabyte” could refer to the quantity of memory (data storage capacity on solid-state drives and Gigabyte External Hard Drives) or data transmission speed. But, it can also be utilized in information technology to indicate the size of RAM. Such as 10,243 bytes. This may cause confusion (and even lawsuits against drive manufacturers within the United States).
In reality, it is the case that in IT and computer science, 1 gigabyte equals 1 073,741,824 (10,243, which is 233.0) bytes. In 2000 it was announced that the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) adopted an International Electrotechnical Council’s (IEC) official acceptance of SI prefixes in metric. For instance, one GB equals one billion bytes, while one Kilobyte (KB) refers to one thousand bits.
In late 1999 in the year 1999, the IEC officially advised that gibi be Giga’s equivalent in metric, replacing the prefix Giga. The 21st-century gibi is the GB term applied depending on the context. Most companies in the field of computer networking use the SI prefix gibi to mean gibibyte (GiB). In referencing the quantity of RAM available, the binary prefix is employed. One GB is 10,243 bytes. If you are referring to memory on disks, one GB is 109 bytes. File systems and software typically define the size of files by using the binary and SI unit mix that includes GB and GiB.
Here are some examples of what a gigabyte of data can translate into:
- About the equivalent of 10 feet of books on the shelf
- More than 100,000 email messages (with no attachments)
- Five hours video-chat
- 350minutes or more of YouTube videos
- 250 songs available on Spotify
- A little less than 8 minutes worth of Ultra HD videos or 1 hour of high-resolution on streaming platforms
- 10 hours on Facebook
- Around 250 photos with a 10-megapixel resolution or 300 images have been uploaded onto social media websites
The cost per GB of storage capacity is based on the type and manufacturer of storage media. However, it has consistently dropped over time. From an average price of $8 for GB of HDD memory, it fell by $0.022 at the end of 2020. It’s more amazing to consider that a single gigabyte of memory was valued at around $500,000 in 1981.
Specifications:
Model GP-A2 Tiny
Dimensions (D x W x H) 78 x 59 x 13 mm
Capacity 160 GB
Weight 80g
Color(s) Charcoal Grey
Serial transfer rate USB 2.0 480Mb/s (MAX)
OS support Mac OS 9.x / Linux 2.4.1.0 / Windows ME above
Accessory Portable HDD / USB cable/ Quick user guide
Warranty One Year Warranty
gigabyte motherboard SSD compatibility

A motherboard is an essential part of pc. It houses all the components necessary for your computer to work and is also responsible for interfacing with the rest of your hardware. If you’ve been shopping for a new motherboard, you may have come across “gigabyte” in the product name. What does this mean and how does it affect compatibility? In this blog post, we’ll explain what Gigabyte motherboard SSD compatibility means and how it can impact your purchase decision. We’ll also provide tips on choosing the correct motherboard for your needs.
What is motherboard SSD compatibility?
A motherboard SSD compatibility refers to the compatibility of a motherboard’s SATA ports and SSDs. Most motherboards have two SATA ports, one for connecting traditional spinning Gigabyte External Hard Drives and the other for connecting M.2 NVMe or PCIe Gen3 x4 SSDs.
The best way to determine if your motherboard has compatible SATA ports is to check the motherboard specifications or look online for user reviews that mention whether specific models of M.2 NVMe or PCIe Gen3 x4 SSDs are compatible with a particular motherboard. Some features that may help with compatibility include support for NVMe protocols (such as AHCI and MSA), UASP, and native SATA 6Gbps support.
Suppose you do not see your desired type of M.2 NVMe or PCIe Gen3 x4 SSD listed among compatible products on the manufacturer’s website or in customer reviews, likely. In that case, your motherboard does not have any such port available. In this case, you will need to purchase an adapter or build a custom PCIe extender cable to connect your SSD to the open port on your motherboard.
Types of SSDs
When choosing the right SSD for your system, there are a few different types to consider. The most popular SSDs are M.2 and SATA III-based, but PCIe and NVMe-based options are also available.
M.2-Based SSDs: M.2 is the newest type of SSD, and it’s based on PCI Express architecture. This means that you can use an M.2 drive in any slot on your motherboard, which is great for laptop users who want to upgrade their storage without replacing their entire system. The best M.2 drives available include the Samsung 850 Pro and the Kingston HyperX Predator PCIe Gen3 x4 M.2 Drive.
SATA III-Based SSDs: SATA III drives were designed for desktop systems, but they’re also compatible with laptops thanks to their small form factor and low-latency connections. They offer faster data transfers than M.2 drives, but they’re less popular because they don’t support PCI Express cards as M.2 drives do. Our favorite SATA III-based SSDs include the ADATA SX930H 2TB and the Crucial MX300 1TB Drives.
PCIe-Based SSDs: PCIe-based SSDs are among the most popular options because they offer high performance and maximum compatibility with all motherboards. They work with both desktop PCs and laptops, making.
How to pick the correct motherboard for your SSD
Purchasing the correct motherboard for your SSD can take time, especially if you have no prior experience building PCs. There are several factors to consider when buying a motherboard for your SSD, including the type of SSD you are using and the chipset used in your PC. This guide will discuss some of the most important factors to consider when choosing a motherboard for your SSD.
If you are using an M.2 NVMe drive, get a motherboard that supports this type of storage. Some motherboards only support SATAIII M.2 drives, which can limit your options if you want to use an NVMe drive.
When it comes to chipset selection, there are two main types of processors: Intel Core and AMD Ryzen chipsets. Most NVMe drives use Intel chipsets, while SATA III M.2 drives typically use AMD chipsets. If you are using an M.2 drive with an Intel chipset, get a motherboard that supports Intel Optane technology. Windows 10 requires Optane movements for certain features to work correctly, such as Miracast streaming from a laptop or desktop to a display over Wi-Fi. If you are using an AMD Ryzen processor and plan on upgrading to an Intel processor in the future, make sure to get a motherboard that supports both processors So you do not have to shop for every other one a while down the road.
Finally, make sure to check whether you have chosen.
How to choose the proper motherboard SSD compatibility?

If you’re looking to buy a new motherboard and storage solution for your computer, there are a few considerations you need to make before choosing the right SSD compatibility. First, ensure your chosen motherboard supports M.2 SATA-III expansion slots. This is because most modern SSDs use this type of connection. Second, make sure the SSD you choose is compatible with the CPU and chipset of your motherboard. Third, be aware of your available ports and possible upgrades. For example, if you have a 3-pin ATX power supply connection, most mainstream 2.5″ SATA III SSDs will not work with your motherboard – you’ll need to look for an M.2 PCIe expansion card or upgrade your power supply. And finally, be prepared to spend extra money – an M.2 PCIe-based SSD will usually cost more than a regular 2.5″ SATA III SSD.
How to check if your motherboard supports a gigabyte SSD?
Your search is over if you want a motherboard supporting the latest and most outstanding gigabyte SSD products. Gigabyte’s Aorus lineup of motherboards is explicitly designed to help gigabyte SSD drives, giving you the best performance and reliability possible.
To ensure compatibility, checking if your computer’s chipset supports gigabyte SSD drives is essential. Most modern computers come equipped with a chipset that supports this type of drive. If your computer doesn’t have a chipset that supports a gigabyte SSD, you’ll need to purchase an appropriate adapter.
Once you’ve verified that your motherboard is compatible with gigabyte SSD drives, it’s time to choose the suitable model for your needs. Gigabyte has a wide range of models available, so there’s bound to be one that fits your budget and meets all of your requirements.
If you’re in the market for a new motherboard, check out Gigabyte’s Aorus lineup!
How to install a gigabyte motherboard SSD on your computer?
Installing a gigabyte motherboard SSD on your computer is easy. Follow these steps to install your new SSD:
• Unscrew the screws that hold your old Gigabyte External Hard Drive in place.
• Remove the old hard drive and plug in the new one.
• Secure the new hard drive with the screws that you removed earlier.
• Reconnect any disconnected cables when you replace the old hard drive.
• Power on your computer and check to see if everything is working correctly.
Which brand is best for an external hard disk?

Brand-wise, both Microsoft and Intel have multiple models of SSDs that are compatible with their respective motherboards. This makes it difficult to determine which brand is best for an external hard disk. Ultimately, the best decision for an external hard disk will come down to what motherboard you have and what type of SSD your motherboard is compatible with.
What is the longest-lasting external drive?
A few factors can affect how long an external drive will last. The most significant factor is how often the industry is accessed. Sparse files, which are smaller versions of files that are stored on the disk, use less space and can reduce the lifespan of a drive. Files frequently accessed, such as pictures or videos, will use more space and can wear down the movement faster.
Another factor affecting a drive’s lifespan is how it is treated. The external drive may eventually fail if exposed to excessive heat. One way to protect a driver from heat exposure is to place it in an airtight case or cabinet when not in use.
Overall, External drives tend to last between 2-5 years depending on how often they’re accessed, how they’re treated, and the type of file being stored on them.
Conclusion
If you’re looking for a motherboard that can support a fast solid-state drive (SSD), then your best bet is to check out the options from Gigabyte. Their motherboards are well-built and typically come with various features that allow them to support a wide range of components, including SSDs. So if you’re in the market for an SSD and want to ensure it’s compatible with your current motherboard, check out Gigabyte’s selection first.
Also, Read Anker Powerline USB 3.0 to micro USB The Premium Durable Cable.





We’re a gaggle of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community.
Your website provided us with valuable information to work on. You have performed a formidable task and our
entire community might be thankful to you.
You actually make it appear so easy along with your presentation however
I to find this matter to be really one thing which I feel I might never understand.
It seems too complicated and very huge for me.
I am looking ahead in your subsequent submit, I’ll try to get the hang of it!
Saved as a favorite, I like your website!
I have read so many posts on the topic of the blogger
lovers but this paragraph is really a good piece of
writing, keep it up.
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Many thanks, However I am having troubles with your RSS.
I don’t know why I cannot subscribe to it. Is there anyone else getting the same RSS
issues? Anybody who knows the answer can you kindly respond?
Thanx!!
I’m truly enjoying the design and layout of your website.
It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much
more enjoyable for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out
a developer to create your theme? Outstanding work!
Blessing
I do agree with all of the ideas you have presented on your
post. They are really convincing and will definitely work.
Nonetheless, the posts are too short for beginners.
May just you please lengthen them a bit from subsequent time?
Thank you for the post.
Thankfulness
When someone writes an piece of writing he/she retains the thought of a user in his/her brain that how a user can be aware of it.
Thus that’s why this piece of writing is great.
Thanks!
Thanksgiving